Antimicrobial Stewardship in Colorado
Antibiotic stewardship is the effort to measure and improve how antibiotics are prescribed by clinicians and used by patients. Improving antibiotic prescribing and use is critical to effectively treat infections, protect patients from harms caused by unnecessary antibiotic use, and combat antibiotic resistance. These programs improve the treatment of infections and reduce negative events and the overuse of antibiotics. The Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment’s (CDPHE) supports antibiotic stewardship by providing effective interventions, treatment guidelines, resources, and support for reporting antibiotic use to the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN).
In 2021, the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment partnered with Children’s Hospital Colorado to start the Colorado Antimicrobial Stewardship Endeavor (CASE). CASE includes physicians, pharmacists, and epidemiologists who provide mentorship and resources to Colorado hospitals that may be new to antibiotic stewardship. CASE provides workshops, consultations, and office hours for hospital antimicrobial stewardship programs. For more information about CASE and how your program can be involved, please visit the CASE webpage.
Firstline houses clinical pathways from Children’s and Denver health along with antimicrobial dosing information, pathogen information, infection prevention information, and more. It is intended for use in all clinical settings. The app is free to download, and is available on iOS and Android devices, as well as a web-based format. CDPHE supports the Firstline app in an effort to provide antimicrobial stewardship treatment guidelines and resources across healthcare settings.
Use the QR code above to find the app. Once downloaded, you can set your location to Denver Health and/or Children’s Hospital Colorado to access all of our materials. Once in the app, clicking on the FirstLine logo in the top left corner will allow you to toggle between locations to access adult vs pediatric guidance. Contact cdphe_hai_ar@state.co.us for more information or feedback.
The CDC’s Priorities for Hospital Core Element Implementation recommend that antimicrobial stewardship programs monitor adherence to facility-specific treatment guidelines for at least one common clinical condition. This monitoring supports the integration of the core elements of action, tracking, and reporting into the clinical pathway.
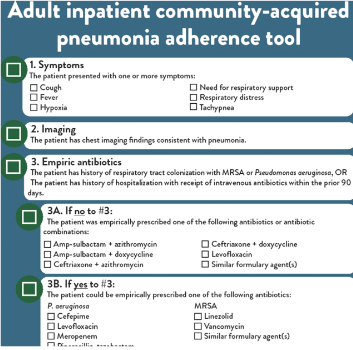
CDPHE created one-page checklists for measuring adherence to common clinical conditions of adult and pediatric community-acquired pneumonia, urinary tract infection, and cellulitis/abscess. Healthcare providers can use these tools during stewardship rounds, point prevalence surveys, or retrospective chart reviews.
Calculate adherence for each condition by reviewing each step of the tool. Adherence to facility treatment guidelines is met by checking the box for each step. These tools were designed to evaluate adherence to pathways in the Firstline mobile application, which can be adapted for use in any facility. The adherence tools should also be useful for facility treatment guidelines other than Firstline. Click on the instructions and any of the tools to learn more!
CDPHE uses a data driven approach that is founded in the principles and best practices of epidemiology, public health, infection prevention, and medicine for all of our stewardship efforts. Data demonstrating trends in stewardship, resistant organisms, and healthcare-associated infections can be found on the HAI data webpage.
Core Elements and Priorities for hospital core element implementation
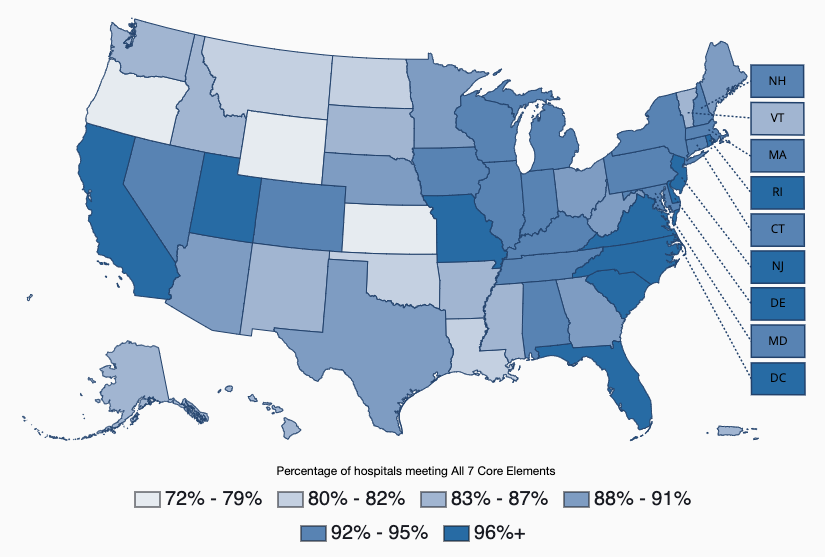
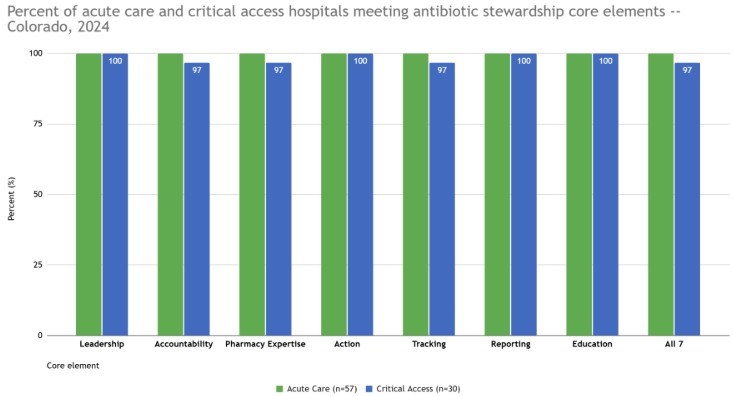
We updated the data reporting engagement with the Core Elements of Antibiotic Stewardship in Colorado hospitals for 2023. Click the image below to find additional details, such as visualization of trends over time, core elements, and priorities for hospital core element implementation.
CDC updated its Antibiotic Resistance and Patient Safety Portal to include Antimicrobial Stewardship trends nationwide and Colorado. This site includes interactive graphs and reports of inpatient and outpatient antibiotic use.
Hospital antibiotic stewardship by state
CDPHE updated the statewide antibiogram to include gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens. This antibiogram reports the percent susceptibility (%S) of antibiotics to bacteria submitted by Colorado hospitals (n=34 hospitals) to the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Antimicrobial Resistance option in 2023.

Please note that the Colorado antibiogram is a tool for antibiotic stewardship and is not intended for clinical use. It should be used in the context of other factors important to improving antibiotic use. Healthcare providers should choose antibiotics based on activity, proven effectiveness, potential for antibiotic resistance or adverse events, and clinical judgment. If you have any questions, please contact cdphe_hai_ar@state.co.us.
CDPHE joins CDC in a national effort to combat the growing threat of antibiotic resistance by asking Colorado health care providers to Be Antibiotics Aware. This year U.S. Antibiotic Awareness Week is November 18-24. CDPHE is participating by providing updated data and resources on the appropriate use of antimicrobials. For more information, visit Antibiotic Awareness | Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment.

The Antimicrobial Use (AU) Option and Antimicrobial Resistance (AR) Option are components of the Antimicrobial Use and Resistance (AUR) Module within the Patient Safety Component of the NHSN. CMS will require hospitals to submit AUR module data beginning calendar year 2024 as a requirement under the Public Health and Clinical Data Exchange objective of the CMS Promoting Interoperability Program.
CDPHE Individual Hospital Reports of Antibiotic Use from NHSN module:
We have created antibiotic use reports which compare individual hospitals to others of similar bed size and region. The reports highlight broad spectrum antibiotic use for targeting antimicrobial stewardship efforts. The de-identified data is exported from the NHSN AU option and shared privately with each hospital ASP.
Quarterly NHSN Office Hours for Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs: Contact cdphe_hai_ar@state.co.us to register for the next AUR Office Hours.
For additional information and steps to fulfill this requirement, visit CDC’s website.
CDPHE supports stewardship in skilled nursing facilities/nursing homes with tools and resources. CDC provides a framework for antimicrobial stewardship with the Core Elements of Antibiotic Stewardship for Nursing Homes. Prescribers, nurses, and other members of a care team can use these resources to support antimicrobial stewardship in nursing homes.
CDPHE Toolkits for Long-term Care Facilities
The LTCF Respiratory Viruses and Antimicrobial Stewardship Toolkit contains links to key resources to support antimicrobial stewardship when respiratory viruses are prevalent.
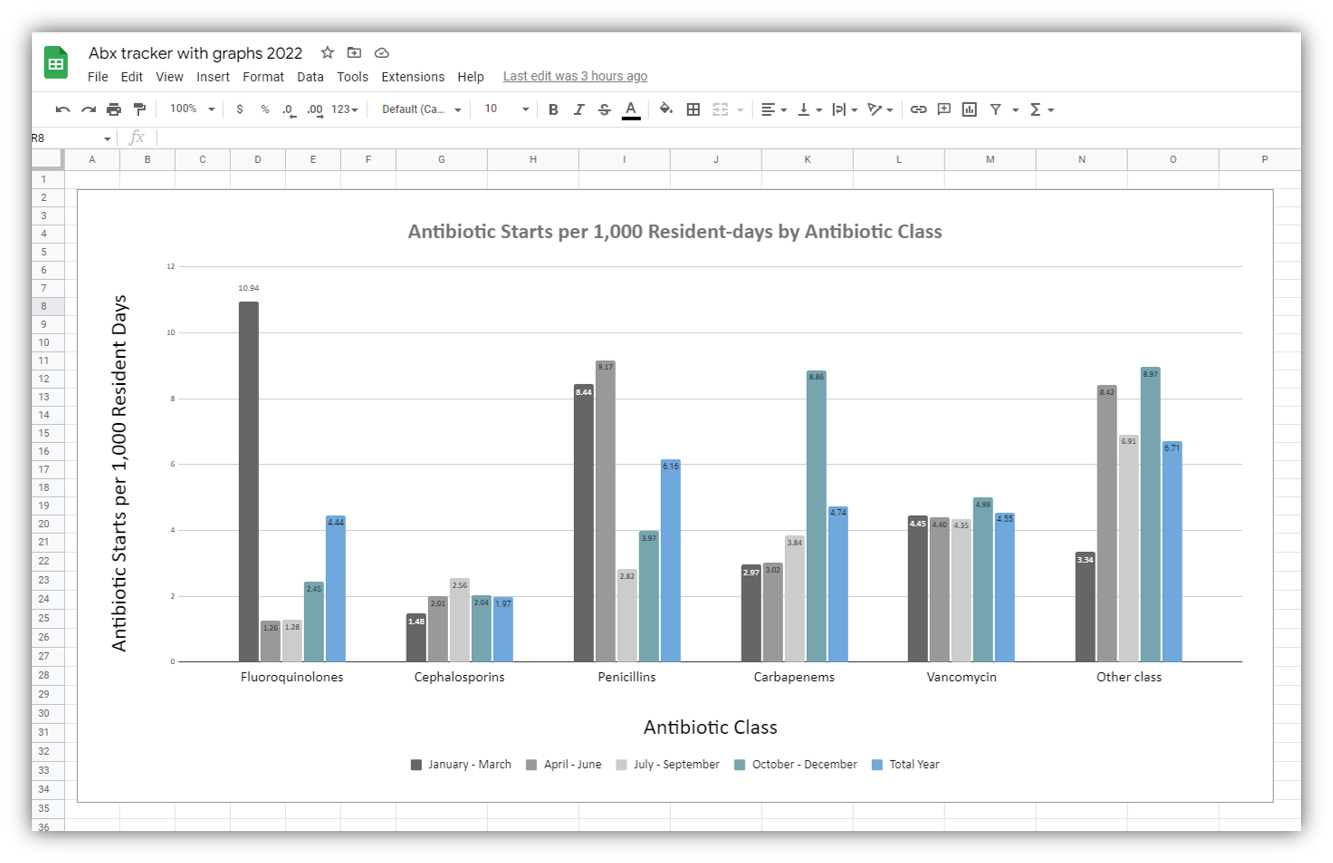
CDPHE’s Antibiotic Tracking Tool for LTCF. CDPHE’s Antibiotic Tracking Tool for LTCF. Please utilize this tool within Google Sheets to track antibiotic usage and infection types among residents. If you need to work with an Excel file of the tool, please email us with your request.
Antibiotic use in nursing homes: a summary of guideline recommendations for common indications. This is a summary of existing published evidence-based guidance for urinary tract infection, community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, and skin and soft tissue infection. This summary is a tool to assist outpatient nursing home antimicrobial stewardship programs to support goals of “right antibiotic,” “right dose,” and “right duration.”
Comparison of testing methods for urinary tract infections wall chart - Urinary tract infections are the most frequently diagnosed infections in the nursing home setting. Use this wall chart and additional information to compare testing methods of urine culture to molecular testing , such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS).
Antibiotic Time-Out Checklist - Use this checklist can be utilized to take a Time-Out to reassess appropriateness of an antibiotic within 48-72 hours after the antibiotic start date.
Suspected Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Action Tool - This resource can guide nursing staff in the initial evaluation of possible UTI in residents without a urinary catheter.

Talking with Residents and Family Members about Antibiotics - AHRQ. This resource provides communication examples for care team staff when discussing UTIs and appropriate use of antibiotics with residents and family members.
Antibiogram quick guide - This one-page resource describes the interpretation and important role of antibiograms in nursing homes.
Colorado nursing home antibiogram
Antibiogram for gram-positive bacteria in nursing homes submitting antimicrobial resistance data - Colorado, 2023 (n=196 nursing homes)
General and specialty dentists are the third highest prescribers of antibiotics in outpatient care settings in the United States.1 As many as 81% of dental antibiotic prescriptions are inappropriate or not indicated.2
This toolkit is a summary of existing published evidence-based guidance to help outpatient dental antimicrobial stewardship programs to support goals of “right antibiotic,” “right dose,” and “right duration.” 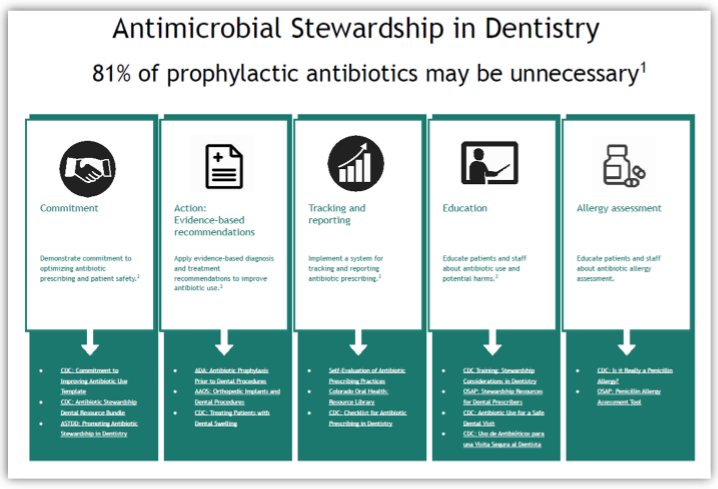
For more information, visit:
- CDC Antibiotic Stewardship Dental Resource Bundle
- Association for Dental Safety: Stewardship Resources for Dental Prescribers
- Colorado Oral Health Resource Library
Guidelines for Antibiotic Use:
Patient Education:
The Core Elements of Antimicrobial Stewardship are a framework for antimicrobial stewardship across healthcare settings. Below are a series of resources for support and development of antimicrobial stewardship programs to perform action, tracking, and reporting within the Core Elements.
CDC’s Core Elements of Antibiotic Stewardship Programs
- Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship Programs
- Core Elements of Outpatient Antibiotic Stewardship
- Core Elements of Antibiotic Stewardship for Nursing Homes
- Implementation of Antibiotic Stewardship Core Elements in Resource-Limited Settings
Additional implementation resources
- Children's Hospital Colorado Professional Resources
- Stenehjem et al. Antibiotic Stewardship in Small Hospitals: Barriers and Potential Solutions. Clin Infect Dis 2017.
- Infectious Diseases Society of America. Implementing an Antibiotic Stewardship Program
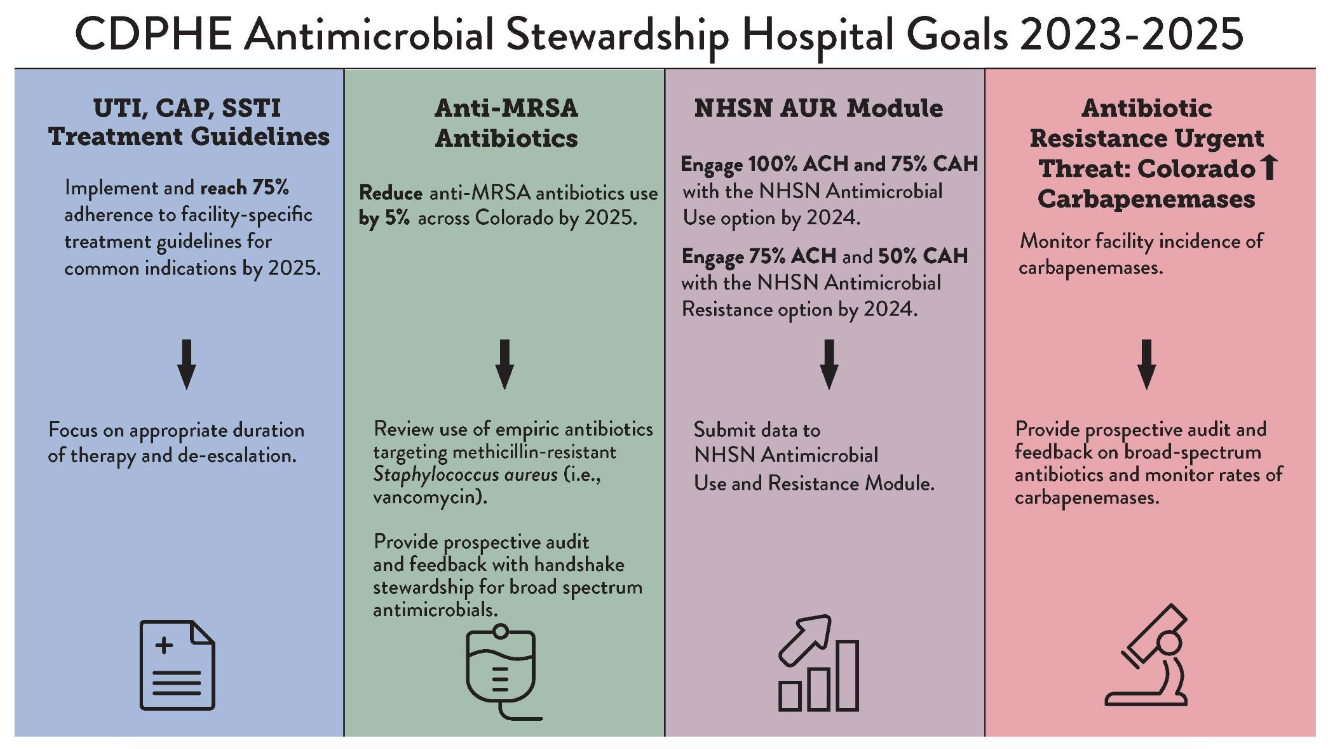
Antimicrobial stewardship (AS) is critical to effectively treat infections and combat antibiotic resistance. The Healthcare-Associated Infections/Antimicrobial Resistance (HAI/AR) program at CDPHE used state-level data to set public health priorities for AS across diverse hospital settings. The CDPHE antimicrobial stewardship hospital goals are described in the infographic below.
Facility-specific clinical practice guidelines serve as a gold standard for antibiotic selection and duration of therapy and are a foundation for antibiotic stewardship program actions. Recommendations should be based on national guidelines but should reflect hospital treatment preferences based on local susceptibilities, treatment options, and patient mix. Facility-specific guidelines should address common indications for antibiotic use, including community-acquired pneumonia, urinary tract infection, skin and soft tissue infection, intra-abdominal infection, and surgical prophylaxis.
- Infectious Diseases Society of America Practice Guidelines
- American Academy of Pediatrics Practice Guidelines
- Sanford Guide (subscription required)
- American Academy of Pediatrics Red Book (subscription required)
Antimicrobial stewardship programs should prioritize actions that are most likely to improve antibiotic use. Some actions that are recommended by evidence-based guidelines include:
- Prospective audit with feedback: An external review of antibiotic therapy by a member of the antibiotic stewardship team, accompanied by suggestions to optimize use, at some point after the agent has been prescribed.
- Handshake stewardship: Rounding-based review of antibiotic therapies by the antibiotic stewardship team with in-person suggestions to optimize use.
- Preauthorization: Prescribers gain approval prior to the use of certain antibiotics designated by the antibiotic stewardship team.
- Infectious Diseases Society of America. Implementing an Antibiotic Stewardship Program
- Tinker et al. Interventions to Optimize Antimicrobial Stewardship. Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology.
- Doernberg et al. Essential Resources and Strategies for Antibiotic Stewardship Programs in the Acute Care Setting. Clin Infect Dis 2018.
- Hurst et al. Handshake Stewardship A Highly Effective Rounding-based Antimicrobial Optimization Service. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2016.
- Tamma et al. What Is the More Effective Antibiotic Stewardship Intervention: Preprescription Authorization or Postprescription Review With Feedback? Clin Infect Dis 2017.
- Anderson et al. Feasibility of Core Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions in Community Hospitals. JAMA Network Open 2019.
- Stenehjem et al. Impact of Implementing Antibiotic Stewardship Programs in 15 Small Hospitals: A Cluster-Randomized Intervention. Clin Infect Dis 2018.
Measurement is critical to identify opportunities for improvement and to assess the impact of interventions. Measurement of antibiotic stewardship interventions may involve evaluation of both processes and outcomes. A priority metric for antibiotic use is antibiotic days of therapy (DOT). DOT is the total number of days for which a specific antibiotic is given. It is usually expressed as a rate per 1,000 patient-days or days present and can be stratified by location of prescription or antibiotic class. Antibiotic use data can also be used to provide feedback to prescribers.
The National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) offers an Antibiotic Use and Resistance Module that allows hospitals to track antibiotic DOT in their facility against national benchmarks and submit data to inform public health priorities. CDPHE created a Frequently Asked Questions guidance document with links to resources from CDC to support hospitals in reporting AUR data to NHSN. CDPHE also offers NHSN AUR Office Hours quarterly. Contact cdphe_hai_ar@state.co.us to register for the next AUR Office Hours. Learn more about tracking antibiotic use from the resources below.
- Benic et al. Metrics for quantifying antibiotic use in the hospital setting: results from a systematic review and international multidisciplinary consensus procedure. J. Antimicrob Chemother 2018.
- Moehring et al. Expert Consensus on Metrics to Assess the Impact of Patient-Level Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions in Acute-Care Settings. Clin Infect Dis 2016.
- Polk et al. Measurement of Adult Antibacterial Drug Use in 130 US Hospitals: Comparison of Defined Daily Dose and Days of Therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2007.
- CDC, National Healthcare Safety Network. Antimicrobial Use and Resistance (AUR) Options.
- CDC, National Healthcare Safety Network. FAQ: Antimicrobial Use (AU) Option
- CDC, National Healthcare Safety Network. AU Case Examples
- CDC, National Healthcare Safety Network. Vendors that have Passed the AU SDS Validation
- CDPHE, NHSN AUR module Frequently Asked Questions and Guidance Document
Antibiotic resistance is a public health threat and a key motivator of antibiotic stewardship. Reporting antibiotic resistance can inform public health priorities, provide targets for antibiotic stewardship in hospitals, and give clinicians information necessary to prescribe appropriate antibiotics for patients. In Colorado, clinical laboratories and health care providers are required to report certain organisms found to be resistant to certain antibiotics to public health. More information about diseases that must be reported and how to report to public health can be found on CDPHE's Report a disease webpage.
- CDC. 2019 AR Threats Report
- CDPHE. HAI Data
- Children’s Hospital Colorado. Bug Watch

- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M39 Analysis and Presentation of Cumulative Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Data, 5th Edition. (purchase required).
- Hindler et al. Analysis and Presentation of Cumulative Antibiograms: A New Consensus Guideline from the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Clin Infect Dis 2007.
- Moehring et al. Challenges in Preparation of Cumulative Antibiogram Reports for Community Hospitals. J Clin Micro 2015.
- CDC, National Healthcare Safety Network. Antimicrobial Use and Resistance (AUR) Options
- CDC, National Healthcare Safety Network. FAQs: Antimicrobial Resistance (AR) Option
See select resources below designed to boost the expertise of antibiotic stewardship program staff and provide education to prescribers and patients.
- CDC. Antibiotic Prescribing and Use
- CDC. Training on Antibiotic Stewardship
- Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Antimicrobial Stewardship Certificate
- Stanford Medicine. Stanford Antimicrobial Stewardship Online CME Courses
- University of Washington, interactive Medical Training Resources (iMTR). Dialogue Around Respiratory Illness Treatment
- New York State Department of Health. Educating Patients About Antibiotic Use. (Youtube video)
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Antibiotic Stewardship Toolkits
Resources for pharmacists:
- Heil EL, et al. The essential role of pharmacists in antimicrobial stewardship. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2016.
- SIDP - Antimicrobial Stewardship Advocacy Toolkit
- CDC. Five Ways Hospital Pharmacists Can Be Antibiotics Aware I Consultant I Community
(New and expanded!) Resources for nurses
Presentation:
Roles of nurses in stewardship:
- Carter EJ, et al. Exploring the nurses’ role in antibiotic stewardship: A multisite qualitative study of nurses and infection preventionists. Am J Infect Control 2018.
- Manning ML, et al. A novel framework to guide antibiotic stewardship nursing practice. Am J Infect Control. 2022;50(1):99-104.
- Monsees E, et al. Implementation of a nurse-driven antibiotic engagement tool in 3 hospitals. Am J Infect Control. 2020;48(12):1415-1421.
- Monsees EA, et al. Integrating bedside nurses into antibiotic stewardship: a practical approach. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2019;40(5):579-584.
Reviews and recommendations:
- Redefining the Antibiotic Stewardship Team: Recommendations from the American Nurses Association and CDC
- Thurman Johnson C, et al. Nurse engagement in antibiotic stewardship programs: a scoping review of the literature. J Healthc Qual. 2023;45(2):69-82.
Resources for providers:
- CDC Antibiotic Stewardship Training Series
- Dialogue Around Respiratory Illness Treatment (DART)
- Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP): Antibiotic Stewardship podcasts and webinars
(New!) Resources for dental and oral health settings:
- CDC Antibiotic Stewardship Dental Resource Bundle
- CDC Checklist for Antibiotic Prescribing in Dentistry
- Colorado Oral Health Resource Library
- OSAP: Stewardship Resources for Dental Prescribers
- Guidelines for Antibiotic Use:
- Patient Education:
Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment
Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance Program
Contact
303-692-2700
Email us with your feedback or questions
cdphe_hai_ar@state.co.us